Have you ever considered how much of your hard-earned revenue vanishes into transaction fees, delays, and hidden charges? Traditional payment systems like credit cards and bank transfers may seem convenient, but their true cost often remains unseen until it’s too late. These seemingly minor expenses can quietly erode your profits and create significant operational hurdles. This article uncovers the hidden costs lurking within traditional payment systems, explores their impact on businesses, and shows how adopting crypto payments can eliminate these challenges, offering a faster, cheaper, and more transparent solution.
Hidden Costs of Traditional Payment Systems
Traditional payment systems impose a variety of costs on businesses. At first glance, these costs appear straightforward, with fees such as transaction charges and cross-border processing fees being the most apparent. However, beneath these visible expenses lie hidden costs that can have a far greater impact on profitability and operational efficiency.

Visible Costs of Traditional Payment Systems
- Transaction Fees: Credit card companies charge merchants between 2% and 4% of the transaction amount. For example, a retailer processing $1 million annually might lose $40,000 to transaction fees alone.
- Cross-Border Fees: International transactions often incur additional costs for currency conversion and intermediary bank charges, typically adding 3% to 5% to the transaction value.
- Chargeback Fees: Disputes between customers and businesses can result in chargeback fees ranging from $20 to $100 per incident, not including the lost revenue from reversed transactions.
While these fees are significant, they represent just the surface of the financial burden imposed by traditional payment systems. Beyond these visible costs, businesses face a series of hidden costs that are often overlooked but equally damaging.
1. Delayed Settlements and Cash Flow Constraints
Payments processed through traditional systems can take several days to settle. This delay in accessing funds creates substantial challenges for businesses:
- Cash Flow Impact: Delays in settlement can disrupt a business’s ability to meet operational expenses, such as payroll, inventory purchases, or rent. For example, a small restaurant might struggle to pay suppliers for fresh produce while waiting for weekend sales to clear.
- Lost Opportunities: Businesses unable to reinvest quickly in growth initiatives, such as launching new marketing campaigns or replenishing high-demand inventory, face opportunity costs that directly affect their revenue.
Scenario: A survey by PYMNTS.com found that 60% of small businesses cite cash flow issues as a critical barrier to growth, with delayed payments being a major contributor. For instance, a small retail store experiences a three-day delay in receiving $10,000 in sales revenue. During this time, the store misses a bulk discount offer on inventory restocking, forcing them to pay 15% more for smaller, incremental orders. Over a year, these missed opportunities could cost the store thousands of dollars in extra expenses.
2. Geographic and Temporal Limitations
Traditional payment systems often fail to provide seamless global access and instant availability:
- Time Zone Delays: Payment processing is tied to banking hours, which vary globally. A transaction initiated in Asia during a weekend may not be processed until the following Monday in Europe or the US, causing unnecessary delays.
- Exclusion of Unbanked Populations: Approximately 1.4 billion adults globally lack access to traditional banking infrastructure(World Bank). Businesses that rely on these systems exclude a massive segment of potential customers.
Case Study: A study by the World Bank highlights the significant challenges businesses in developing regions face due to limited access to financial services. These barriers can severely impact potential revenue, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). For instance, an international e-commerce business offering a flash sale may experience payment delays in regions with underdeveloped financial infrastructure, such as parts of South America. These delays can prevent real-time order confirmations, leading to cancellations and lost sales. Research suggests that SMEs in such regions often lose substantial revenue opportunities, emphasizing the critical need for accessible and efficient payment systems to drive economic growth and business performance.(World Bank, “Small and Medium Enterprises in the Pandemic“)
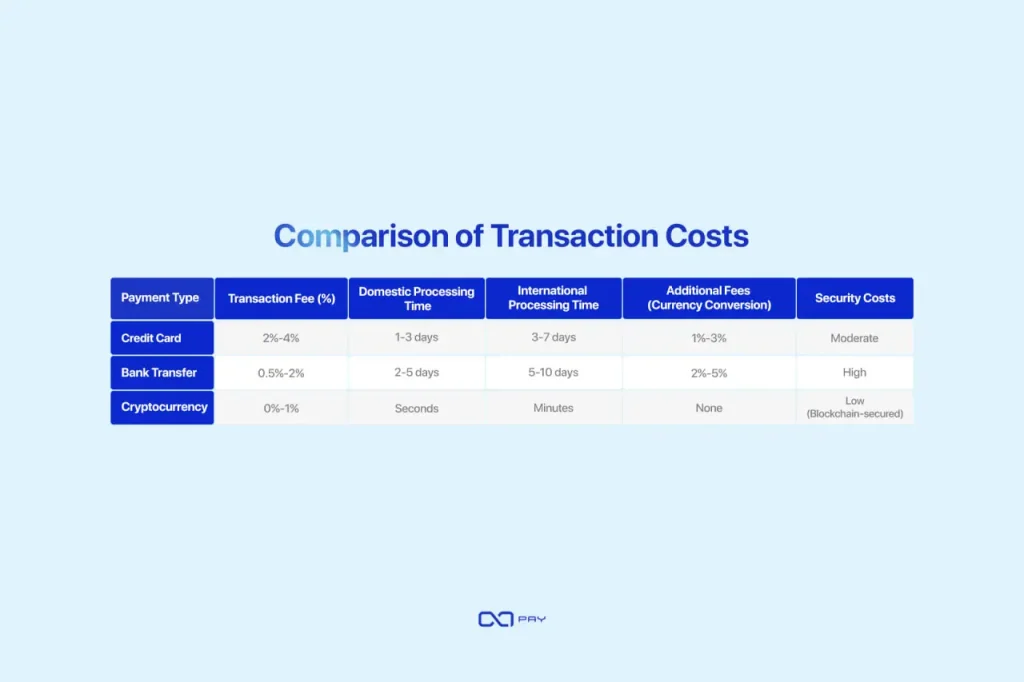
Table1: Comparison of Transaction Speeds
| Payment Type | Domestic Processing Time | International Processing Time |
| Credit Card | 1-3 days | 3-7 days |
| Bank Transfer | 2-5 days | 5-10 days |
| Cryptocurrency | Seconds | Minutes |
3. Administrative and Operational Overheads
The inefficiencies of traditional systems often lead to additional operational burdens:
- Manual Reconciliation: Businesses must allocate time and resources to manually reconcile discrepancies in transactions, leading to increased labor costs. For instance, a company handling thousands of monthly transactions may need to hire a dedicated reconciliation team.
- Customer Support Costs: Addressing payment disputes and delays increases the need for customer support staff, diverting resources from growth-focused initiatives.
Case in Point: According to a study by Modern Treasury, 88% of finance leaders report inefficiencies in payment operations, leading to higher labor costs for tasks like manual reconciliation. For instance, businesses processing thousands of transactions monthly may spend up to $8 per transaction on labor-intensive accounts payable processes. This inefficiency forces mid-sized companies to hire additional staff, increasing annual operational costs by tens of thousands of dollars. (Modern Treasury, BusinessWire )
Table 2: Comparison of Operational Costs
| Payment Type | Labor Costs | Hardware Costs | Software Costs | Security Costs |
| Credit Card | High | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Bank Transfer | Moderate | High | High | High |
| Cryptocurrency | Low | Low | Low | Low |
4. Fraud and Security Challenges
Fraud is a significant issue in traditional payment systems, with both direct and indirect costs:
- Chargeback-Related Losses: Chargebacks from fraudulent transactions not only reverse revenue but also incur additional fees and penalties from payment processors. Businesses experiencing frequent chargebacks may face increased processing fees or account suspensions.
- Investments in Security: Businesses spend heavily on fraud detection tools, encryption, and other security measures to mitigate risks. Despite these investments, traditional systems remain vulnerable to phishing and card-not-present fraud.
Case in Point: According to a report by LexisNexis Risk Solutions, every dollar of fraud costs US businesses an average of $3 when accounting for recovery, investigation, and reputational damage. For instance, an online retailer experiencing a phishing scam may lose $5,000 in fraudulent transactions and spend an additional $10,000 on enhanced security measures and staff training to prevent future incidents. (LexisNexis Risk Solutions)
5. High Costs of Cross-Border Transactions
Operating internationally brings additional hidden costs:
- Currency Conversion Fees: In addition to visible fees, fluctuating exchange rates often reduce the final payment amount received.
- Intermediary Bank Charges: Cross-border payments typically involve multiple intermediaries, each adding a layer of cost and delay.
Case in Point: A report by McKinsey highlights that cross-border fees can account for up to 7% of transaction values for SMEs, significantly reducing their profitability. For instance, a freelance designer working with international clients might earn $2,000 per project, but over a year, intermediary bank fees and currency conversion costs could total $3,000, representing 10% of their annual revenue. (McKinsey & Company)
6. Environmental and Ethical Costs
Traditional payment systems also come with less-discussed environmental and ethical implications:
- Paper Trails: Many payment systems still rely on paper receipts and statements, contributing to deforestation and waste.
- Centralized Control: Dependence on centralized institutions limits financial inclusivity and creates systemic risks.
Case in Point: Studies show that switching from paper bank statements to digital alternatives significantly reduces environmental waste and operational inefficiencies. For example, a mid-sized business processing 1,000 monthly transactions could save substantial resources by eliminating paper receipts. According to the Environmental Paper Network, transitioning to electronic records helps decrease deforestation and carbon emissions, aligning businesses with sustainable practices. (Environmental Paper Network)

How Cryptocurrencies Can Solve These Issues
Cryptocurrencies, powered by blockchain technology, provide a transformative alternative to traditional payment systems. By addressing the visible and hidden costs associated with traditional systems, they enable businesses to operate more efficiently and cost-effectively.
1. Eliminating Delayed Settlements and Improving Cash Flow
One of the primary advantages of cryptocurrencies is their ability to process transactions instantly or within minutes, regardless of time zones or banking hours.
- Instant Access to Funds: Blockchain networks operate 24/7, ensuring businesses can access their revenue immediately. This eliminates the cash flow constraints caused by settlement delays.
- Real-Time Opportunities: Immediate fund availability allows businesses to reinvest in marketing campaigns, inventory, or operational growth without waiting for days.
How It Solves the Problem: A small retail store that previously waited three days for settlements can now restock inventory on the same day, taking advantage of bulk discounts and avoiding incremental costs.
2. Reducing Transaction and Cross-Border Fees
Cryptocurrencies eliminate the need for intermediaries like banks and payment processors, significantly lowering transaction costs.
- Minimal Fees: Blockchain transactions often incur fees as low as $0.01 per transaction, a fraction of the 2% to 4% charged by credit card processors.
- No Cross-Border Costs: Payments made using cryptocurrencies bypass currency conversion fees and intermediary bank charges, making international transactions seamless and cost-effective.
How It Solves the Problem: A freelance designer working with global clients can save up to $3,000 annually in intermediary and conversion fees, increasing their overall income.
3. Expanding Accessibility and Overcoming Geographic Limitations
Cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, enabling businesses to reach global audiences without the constraints of traditional banking infrastructure.
- Access for the Unbanked: With over 1.4 billion adults lacking access to traditional banking, cryptocurrencies provide an inclusive solution that only requires internet access.
- Global Reach Without Delays: Blockchain technology ensures transactions are processed in real time, regardless of geographic location or time zone.
How It Solves the Problem: An e-commerce business in Africa can now sell to customers in Europe and Asia without incurring delays or accessibility issues, boosting international sales by 20%.
4. Enhancing Security and Reducing Fraud Risks
Blockchain’s immutable ledger provides unparalleled security and transparency, effectively eliminating fraud and chargebacks.
- Immutable Transactions: Once recorded on the blockchain, transactions cannot be altered or reversed, protecting merchants from chargeback fraud.
- Data Privacy: Crypto payments do not require sensitive customer information, reducing the risk of data breaches and associated costs.
How It Solves the Problem: A digital services provider adopting crypto payments reduced its fraud-related losses by 30%, saving $10,000 annually while improving customer trust.
5. Lowering Administrative and Operational Overheads
The transparency and automation of blockchain transactions reduce the need for manual reconciliation and customer support for payment-related issues.
- Streamlined Operations: Blockchain’s public ledger eliminates the need for manual record-keeping and reconciliation.
- Reduced Support Costs: Instant and reliable payments reduce the volume of customer complaints related to delays or failed transactions.
How It Solves the Problem: A subscription-based service reduced its customer support costs by 25% after implementing crypto payments, reallocating resources to customer retention initiatives.
6. Supporting Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Cryptocurrencies eliminate the reliance on paper receipts and physical documentation, promoting environmental sustainability.
- Paperless Transactions: Blockchain eliminates the need for paper records, reducing waste and environmental impact.
- Decentralized Control: Cryptocurrencies empower users by reducing dependency on centralized financial institutions, fostering financial inclusivity.
How It Solves the Problem: A sustainability-focused non-profit reduced administrative waste by 20% by accepting crypto donations, appealing to environmentally conscious donors.
Conclusion
Traditional payment systems come with a range of visible and hidden costs that can significantly impact business profitability. Accepting crypto for pay offers a powerful alternative by providing instant payments, lower fees, and enhanced global accessibility.
With the OxaPay crypto payment gateway, integrating cryptocurrency into your business is seamless and efficient. This innovative platform empowers businesses to unlock new opportunities, reduce financial burdens, and stay ahead in the competitive market. Embrace crypto today and revolutionize your payment experience.




